Book Value per Share Formula How to Calculate BVPS?
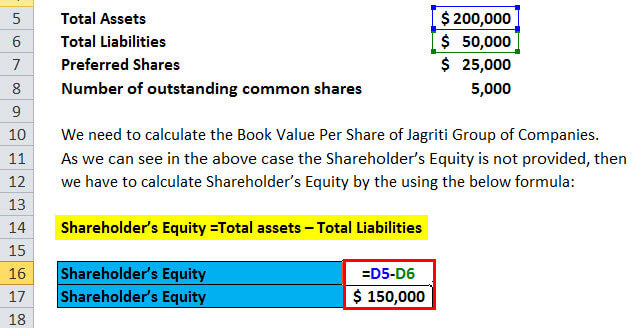
Please note that past performance of financial products and instruments does not necessarily indicate the prospects and performance thereof. The price of a single publicly traded stock divided by the number of shares outstanding gives us the market price per share. While BVPS is set at a certain price per share, the market price per share varies depending purely on supply and demand in the market. Some investors may use the book value per share to estimate a company’s equity-based on its market value, which is the price of its shares.

Formula and Calculation of the Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions. Many investors use the price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio) to compare a firm’s market capitalization to its book value and locate undervalued companies. This ratio is calculated by dividing the company’s current stock price per share by its book value per share (BVPS).
Want to start your Investment Journey?
- You need to find the company’s balance sheet to obtain total assets, total liabilities, and outstanding shares.
- 5paisa will not be responsible for the investment decisions taken by the clients.
- On the other hand, a declining book value per share could indicate that the stock’s price may decline, and some investors might consider that a signal to sell the stock.
- Critics of book value are quick to point out that finding genuine book value plays has become difficult in the heavily-analyzed U.S. stock market.
- This may be a more useful valuation measure when valuing something like a patent in different ways or if it is difficult to put a value on such an intangible asset in the first place.
- Rather than buying more of its own stock, a company can use profits to accumulate additional assets or reduce its current liabilities.
The book value per share is just one metric that you should look at when considering an investment. It’s important to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision. The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books. Alternatively, another method to increase the BVPS is via share repurchases (i.e. buybacks) from existing shareholders. Therefore, the amount of cash remaining once all outstanding liabilities are paid off is captured by the book value of equity. If a company is selling 15% below book value, but it takes several years for the price to catch up, then you might have been better off with a 5% bond.
The Difference Between Book Value per Share and Net Asset Value (NAV)
Large discrepancies between the P/B ratio and ROE often raise a red flag for investors. The book value meaning or the origination of the name comes from the accounting lingo where the balance sheet of a company was called ‘books’. The P/B ratio, alternatively referred to as the price-equity ratio, is calculated based on the value of a company. Despite its importance, it can be intimidating for those not familiar with financial jargon.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: Meaning, Formula, and Example
Let’s have a look at a hypothetical example of an ABC Ltd company’s balance sheet to understand the BVPS of an asset. On the other hand, if a company with outdated equipment has consistently put off repairs, those repairs will eat into profits at some future date. This tells you something about book value as well as the character of the company and its management. You won’t get this information from the P/B ratio, but it is one of the main benefits of digging into the book value numbers and is well worth the time. That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company.
This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated. To calculate book value per share, simply divide a company’s total common equity by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if a company has total common equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding, then its book value per share would be $1.
As noted above, another way to calculate book value is to subtract a business’ total liabilities from its total assets. The price-to-book ratio is important because it can help investors understand whether a company’s market price seems reasonable compared to its balance sheet. To calculate the book value of a company, subtract the total liabilities from the total assets.
This means that, in the worst-case scenario of bankruptcy, the company’s assets will be sold off and the investor will still make a profit. There are many methods that investors can use to evaluate the value of a company. By leveraging useful and insightful formulas such as a company’s Book Value Per Share, investors can determine states with no income tax a company’s value relative to its current market price. Whereas some price models and fundamental analyses are complex, calculating book value per share is fairly straightforward. At its core, it’s subtracting a company’s preferred stock from shareholder equity and dividing that sum by the average amount of outstanding shares.
If a business is presently trading at $20 but has a book value of $10, it is being sold for double its equity. If you observe the formula for book value per share, you will notice that the denominator governs the value of the resultant. Book value per share also tells you about whether or not the stock you are purchasing is undervalued. On the other hand, the weighted average shares outstanding is a different number that accounts for the changes in total shares outstanding. All the new issuances and buybacks that happen during a set term are accounted for in the weighted average shares outstanding when calculating book value per share, making it a more reliable, true number. Comparing the book value per share of a company with its market value per share helps investors measure its true value.
Book value per share tells you the true status of the shares of a company with respect to their price on the market. You can invest in stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, and more. SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here). The following image shows Coca-Cola’s “Equity Attributable to Shareowners” line at the bottom of its Shareowners’ Equity section. It’s one metric that an investor may look for if they’re interested in valuating Coca-Cola as a potential investment.
But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong. The difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities is its net asset value, or the value remaining for equity shareholders. The company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, its common equity increases along with BVPS.